In order to adapt to the increasing international attention to environmental protection, PCBA changed from lead to lead free process, and applied new laminate materials, these changes will cause PCB electronic products solder joint performance changes. Because component solder joints are very sensitive to strain failure, it is essential to understand the strain characteristics of PCB electronics under the harshest conditions through strain testing.
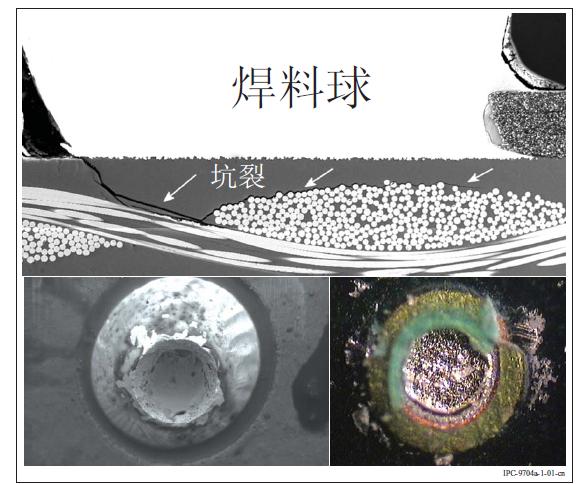
For different solder alloys, package types, surface treatments or laminate materials, excessive strain can lead to various modes of failure. Failures include solder ball cracking, wiring damage, laminate related bonding failure (pad skewing) or cohesion failure (pad pitting), and package substrate cracking (see Figure 1-1). The use of strain measurement to control the warping of printed boards has proven beneficial to the electronics industry and is gaining acceptance as a way to identify and improve production operations.
Strain testing provides an objective analysis of the level of strain and strain rate that SMT packages are subjected to during PCBA assembly, testing, and operation, providing a quantitative method for PCB warpage measurement and risk rating assessment.
The goal of strain measurement is to describe the characteristics of all assembly steps involving mechanical loads.
Post time: Apr-19-2024